Introduction
In March 2025, we discovered Operation ForumTroll, a series of sophisticated cyberattacks exploiting the CVE-2025-2783 vulnerability in Google Chrome. We previously detailed the malicious implants used in the operation: the LeetAgent backdoor and the complex spyware Dante, developed by Memento Labs (formerly Hacking Team). However, the attackers behind this operation didn’t stop at their spring campaign and have continued to infect targets within the Russian Federation.
Emails posing as a scientific library
In October 2025, just days before we presented our report detailing the ForumTroll APT group’s attack at the Security Analyst Summit, we detected a new targeted phishing campaign by the same group. However, while the spring cyberattacks focused on organizations, the fall campaign honed in on specific individuals: scholars in the field of political science, international relations, and global economics, working at major Russian universities and research institutions.
The emails received by the victims were sent from the address support@e-library[.]wiki. The campaign purported to be from the scientific electronic library, eLibrary, whose legitimate website is elibrary.ru. The phishing emails contained a malicious link in the format: https://e-library[.]wiki/elib/wiki.php?id=<8 pseudorandom letters and digits>. Recipients were prompted to click the link to download a plagiarism report. Clicking that link triggered the download of an archive file. The filename was personalized, using the victim’s own name in the format:
A well-prepared attack
The attackers did their homework before sending out the phishing emails. The malicious domain, e-library[.]wiki, was registered back in March 2025, over six months before the email campaign started. This was likely done to build the domain’s reputation, as sending emails from a suspicious, newly registered domain is a major red flag for spam filters.
Furthermore, the attackers placed a copy of the legitimate eLibrary homepage on https://e-library[.]wiki. According to the information on the page, they accessed the legitimate website from the IP address 193.65.18[.]14 back in December 2024.
A screenshot of the malicious site elements showing the IP address and initial session date
The attackers also carefully personalized the phishing emails for their targets, specific professionals in the field. As mentioned above, the downloaded archive was named with the victim’s last name, first name, and patronymic.
Another noteworthy technique was the attacker’s effort to hinder security analysis by restricting repeat downloads. When we attempted to download the archive from the malicious site, we received a message in Russian, indicating the download link was likely for one-time use only:

The message that was displayed when we attempted to download the archive
Our investigation found that the malicious site displayed a different message if the download was attempted from a non-Windows device. In that case, it prompted the user to try again from a Windows computer.
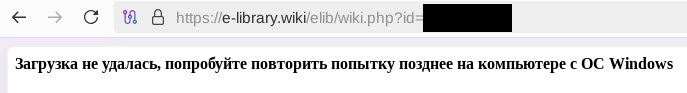
The message that was displayed when we attempted to download the archive from a non-Windows OS
The malicious archive
The malicious archives downloaded via the email links contained the following:
- A malicious shortcut file named after the victim:
_ _ .lnk - A
.Thumbsdirectory containing approximately 100 image files with names in Russian. These images were not used during the infection process and were likely added to make the archives appear less suspicious to security solutions.
A portion of the .Thumbs directory contents
When the user clicked the shortcut, it ran a PowerShell script. The script’s primary purpose was to download and execute a PowerShell-based payload from a malicious server.

The script that was launched by opening the shortcut
The downloaded payload then performed the following actions:
- Contacted a URL in the format:
https://e-library[.]wiki/elib/query.php?id=<8 pseudorandom letters and digits>&key=<32 hexadecimal characters>to retrieve the final payload, a DLL file. - Saved the downloaded file to
%localappdata%\Microsoft\Windows\Explorer\iconcache_<4 pseudorandom digits>.dll. - Established persistence for the payload using COM Hijacking. This involved writing the path to the DLL file into the registry key HKCR\CLSID\{1f486a52-3cb1-48fd-8f50-b8dc300d9f9d}\InProcServer32. Notably, the attackers had used that same technique in their spring attacks.
- Downloaded a decoy PDF from a URL in the format:
https://e-library[.]wiki/pdf/<8 pseudorandom letters and digits>.pdf. This PDF was saved to the user’s Downloads folder with a filename in the format:_ _ .pdf
The decoy PDF contained no valuable information. It was merely a blurred report generated by a Russian plagiarism-checking system.
A screenshot of a page from the downloaded report
At the time of our investigation, the links for downloading the final payloads didn’t work. Attempting to access them returned error messages in English: “You are already blocked…” or “You have been bad ended” (sic). This likely indicates the use of a protective mechanism to prevent payloads from being downloaded more than once. Despite this, we managed to obtain and analyze the final payload.
The final payload: the Tuoni framework
The DLL file deployed to infected devices proved to be an OLLVM-obfuscated loader, which we described in our previous report on Operation ForumTroll. However, while this loader previously delivered rare implants like LeetAgent and Dante, this time the attackers opted for a better-known commercial red teaming framework: Tuoni. Portions of the Tuoni code are publicly available on GitHub. By deploying this tool, the attackers gained remote access to the victim’s device along with other capabilities for further system compromise.
As in the previous campaign, the attackers used fastly.net as C2 servers.
Conclusion
The cyberattacks carried out by the ForumTroll APT group in the spring and fall of 2025 share significant similarities. In both campaigns, infection began with targeted phishing emails, and persistence for the malicious implants was achieved with the COM Hijacking technique. The same loader was used to deploy the implants both in the spring and the fall.
Despite these similarities, the fall series of attacks cannot be considered as technically sophisticated as the spring campaign. In the spring, the ForumTroll APT group exploited zero-day vulnerabilities to infect systems. By contrast, the autumn attacks relied entirely on social engineering, counting on victims not only clicking the malicious link but also downloading the archive and launching the shortcut file. Furthermore, the malware used in the fall campaign, the Tuoni framework, is less rare.
ForumTroll has been targeting organizations and individuals in Russia and Belarus since at least 2022. Given this lengthy timeline, it is likely this APT group will continue to target entities and individuals of interest within these two countries. We believe that investigating ForumTroll’s potential future campaigns will allow us to shed light on shadowy malicious implants created by commercial developers – much as we did with the discovery of the Dante spyware.
Indicators of compromise
e-library[.]wiki
perf-service-clients2.global.ssl.fastly[.]net
bus-pod-tenant.global.ssl.fastly[.]net
status-portal-api.global.ssl.fastly[.]net
